Phonics is the way in which children begin to understand words, and as such is one of the most important parts of a child’s early education.
This blog will go over the basic principles of phonics and the terms used, to help better understand the subject and consequently help children learn more effectively.
Phonics deals with phonemes; the smallest unit of sound. Though there are only 26 letters in the English Alphabet, there are 44 phonemes. We’ve listed them below along with an example of how they sound;
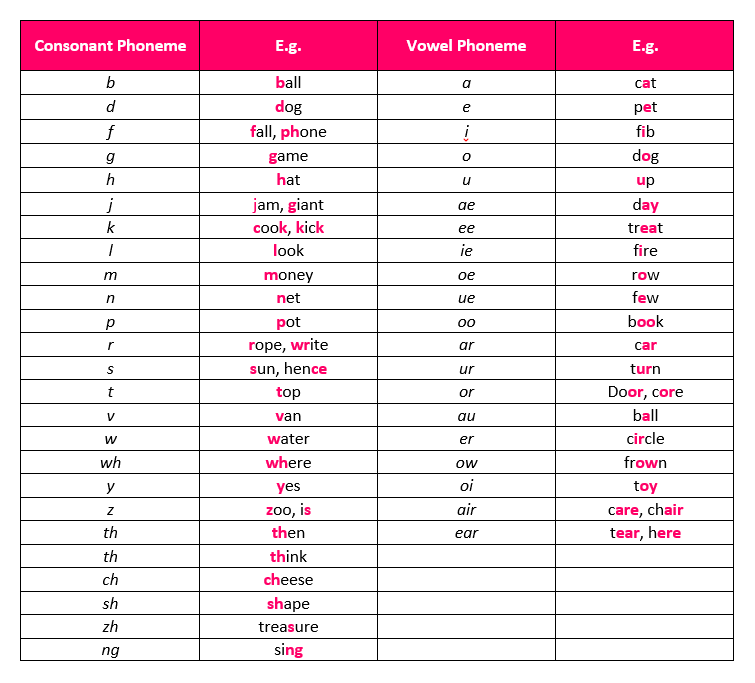
One of the main difficulties children face with learning to read using phonics is disparity between letters and sounds, and how some sounds can be represented through different letters. For example, ‘Where’ ‘Wear’ and ‘Ware’ are all pronounced the same, but have different meanings and different letters. The phoneme ‘air’ is represented by three different spellings; ‘ere’, ‘ear’ and ‘are’. Words with the same pronunciation but different meanings or spellings are called homophones.
Though there are rules to follow, there are also exceptions which make practice crucial to learning. The more often children come up against ‘tricky words’ and rules, the more likely they are to learn the irregularities.
Phonics aims to aid children’s reading and writing skills by helping them sound out words, isolating individual ‘phonemes’ and linking them together logically to form words.
This logical learning process allows for quick progression, but only if the basics are learnt first. A strong foundation is needed, otherwise children can easily get lost and lose confidence in their reading abilities. Going slowly and reinforcing new sounds repeatedly through games, activities and worksheets will help children gain confidence in sounding out letters and making connections.
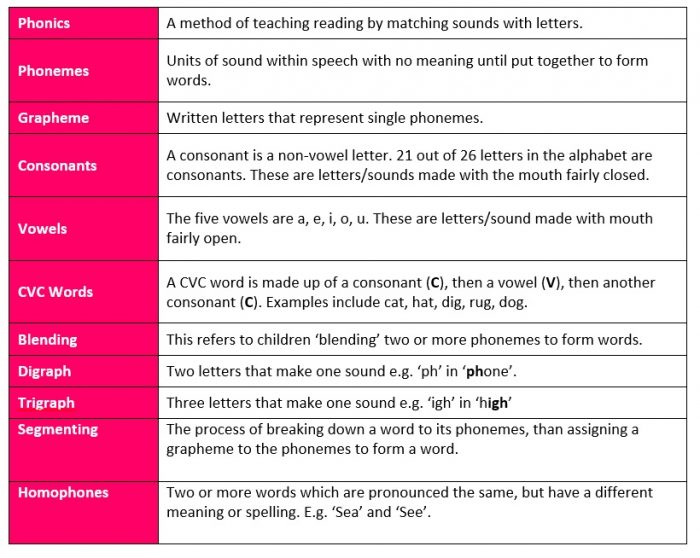
To help learn the lingo of phonics, we’ve put together a handy glossary of terms you might come across;